Atherosclerosis diagnosis and management with Melbourne Heart Care
Melbourne Heart Care is dedicated to providing comprehensive care and support for those people diagnosed with atherosclerosis. Our team of experienced cardiologists are here to help you understand your condition, manage your heart health and guide you towards a healthier future.
Contact Melbourne Heart Care for a personalised treatment plan to manage your atherosclerosis.
What is atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis develops slowly over time and causes hardening of the arteries, the blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood and nutrients throughout your body. It is the most common cause of cardiovascular disease and puts people at an increased risk of heart attack.
It can come in several different forms:
- Coronary artery disease – where it affects the coronary arteries that supply blood and oxygen to your heart muscle
- Carotid artery disease – where plaque buildup occurs in the arteries that supply your brain
- Peripheral artery disease – usually occurs in the arteries that supply blood to your legs and lower extremities
- Renal artery stenosis – a vascular disease that blocks blood flow to your kidneys
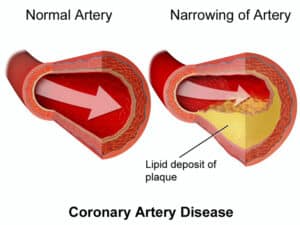
Atherosclerosis symptoms – the atherosclerotic disease develops over time, with lipid and plaque build-up gradually causing a reduced flow of blood through the artery.
What causes atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis begins with a gradual buildup of fatty deposits, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances on the inner walls of your arteries. Over time, these deposits, known as plaques, can harden and narrow your arteries, reducing blood flow or even resulting in blocked arteries.
What are the risk factors for atherosclerosis?
There are many risk factors for atherosclerosis, and they can be categorised into modifiable, non-modifiable and medical conditions.

An unhealthy diet and smoking are two of the biggest contributors to fatty deposits, plaque buildup and high cholesterol. By changing these unhealthy choices you can significantly lower your risk of developing atherosclerosis.
Modifiable risk factors
These are risks that you can change to improve your overall health and reduce your risk of developing atherosclerosis:
- Unhealthy diet that is high in saturated fats and sugars
- Smoking
- Obesity/overweight
- Sedentary lifestyle
Non-modifiable risk factors
These are things that you cannot change:
- Age
- Family history
- Gender (men have a higher risk after age 45, and females after menopause)
Medical conditions
Some medical conditions can increase your risk of developing atherosclerosis:
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Hypercholesterolemia (high cholesterol)
- Diabetes
What are atherosclerosis symptoms?
Atherosclerosis is often referred to as a “silent” disease, as in the early stages you may not experience any symptoms. Once the blood vessels have narrowed over 70%, blood flow is significantly restricted or a blood clot completely blocks the blood vessels, symptoms of atherosclerosis will emerge.
This means that most people may not notice atherosclerosis symptoms until it results in a medical emergency, such as a heart attack or stroke. The specific symptoms of atherosclerosis vary depending on which arteries are affected:
- Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease may lead to chest pain or pressure known as angina. You may also experience some shortness of breath, dizziness or fatigue.
- Carotid artery disease can cause stroke or TIA symptoms, such as difficulty speaking or slurred speech, visual changes, and drooping facial muscles.
- Peripheral artery disease presents with numbness or weakness in the legs, leg pain when walking or exercising (claudication) and decreased blood flow and blood pressure to the feet and legs.
Recognising and addressing these symptoms promptly is vital for managing atherosclerosis and preventing complications.
What are the complications of atherosclerosis?
There are several complications associated with atherosclerosis that constitute medical emergencies. These arise when a plaque buildup bursts, causing a blood clot to form and completely block blood flow in that blood vessel, or travel to a different part of the body. This may result in:
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia)
- Tissue death and severe pain in lower limbs when there’s no blood flow through a blocked artery

Heart attack and stroke are potential complications of this disease, where a blood vessel is completely (or almost) blocked, meaning not enough blood and oxygen are delivered to your heart or brain.
How is atherosclerosis diagnosed?
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management. Melbourne Heart Care employs various tests and procedures to diagnose atherosclerosis, including:
- Physical examination to identify weak pulses in your peripheries, a bruit (whooshing sound that blood flow makes as it travels through a blocked artery), delayed wound healing, poor capillary refill, pale or blue fingers or toes
- Discussing your family history and current medical conditions to determine risk factors
- Blood tests to measure cholesterol levels
- Doppler ultrasound provides images of your artery walls
- ECG (electrocardiogram) shows the electrical activity in your heart and can identify any areas that may have decreased blood flow
- A stress test can monitor your heart rate and blood pressure when exercising to see how your heart performs under pressure and if there’s any reduced blood flow
- CT angiogram or MRI to provide highly detailed images of blood vessels
- CT calcium score shows how much calcium is in your coronary arteries and provides a risk score for developing heart disease
- Percutaneous coronary intervention, or a coronary angiogram, can provide an in-depth analysis of the arteries in your heart
What are the treatment options for atherosclerosis?
There are a range of options to treat atherosclerosis, depending on what blood vessels are affected, your symptoms and your underlying medical conditions or risk factors.
Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle that incorporates a balanced, nutritious diet, regular exercise, no smoking, and managing stress can slow the progression of atherosclerosis and prevent medical conditions such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol or obesity.
Medications: Prescription medications may be recommended to treat high cholesterol, lower blood pressure, and prevent blood clots.
Interventional procedures: In some cases, procedures can be performed to open blocked arteries:
- Carotid endarterectomy – a surgical procedure that opens a blocked carotid artery, restoring proper blood flow to the brain
- Coronary angiogram with stents – a procedure to open up blocked coronary arteries and restore flow to the heart muscle
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) – open heart surgery that uses blood vessels from other areas of your body to bypass a blocked coronary artery
- Endovascular treatment – minimally invasive procedures to remove blockages or stent areas where the artery narrows
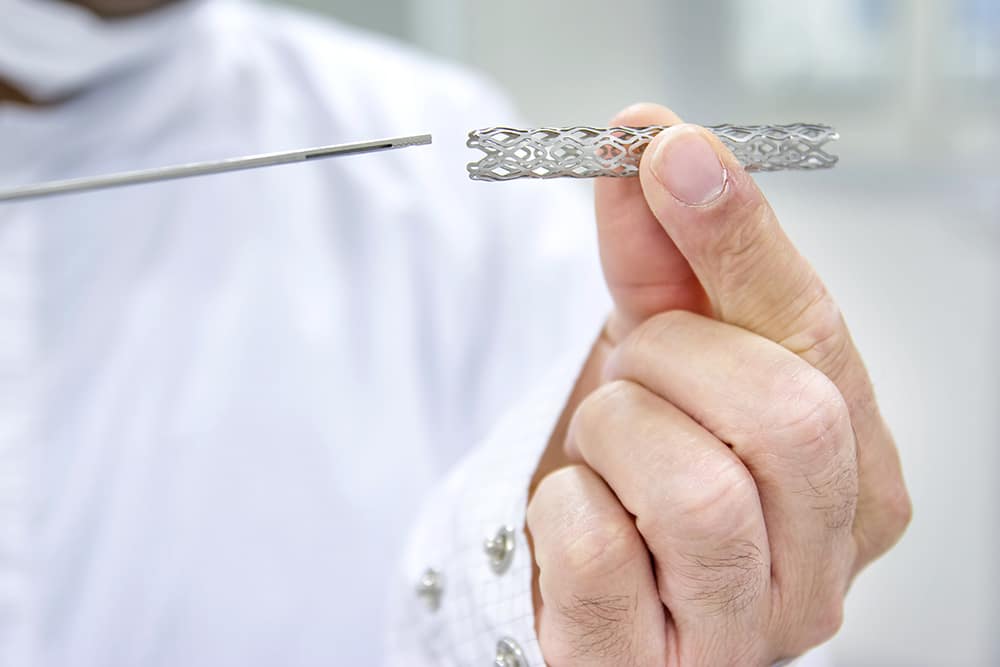
There are a range of treatment options, from making healthier choices to medications and interventions such as a cardiac stent.
Melbourne Heart Care offers diagnosis and treatment for atherosclerosis
Melbourne Heart Care stands out as the premier choice for atherosclerosis treatment in Melbourne. Our team of specialists brings extensive expertise to the table, delivering personalised care tailored to your unique needs. We offer state-of-the-art facilities, a full range of services, and a multidisciplinary approach that encompasses diagnostics, interventions, and follow-up care.

